Ongoing Subjects
Data Communications
Human beings are the only creatures on the earth who are able to communicate with each other through the medium of language. But humans take this gift to another extent. Distance, time, and physical existence of the person don’t matter in communication these days because they build a communication system through which they can communicate or share data like images, videos, text, files, etc with their loved ones anytime anywhere. Communication is defined as a process in which more than one computer transfers information, instructions to each other and for sharing resources. Or in other words, communication is a process or act in which we can send or receive data. A network of computers is defined as an interconnected collection of autonomous computers. Autonomous means no computer can start, stop or control another computer.
Components of Data Communication
A communication system is made up of the following components:
- Message: A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted from one person to another. It could be a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
- Sender: It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or workstation, etc.
- Receiver: It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer, telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
- Transmission Medium / Communication Channels: Communication channels are the medium that connect two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media.
- Set of rules (Protocol): When someone sends the data (The sender), it should be understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is meaningless. For example, Sonali sends a message to Chetan. If Sonali writes in Hindi and Chetan cannot understand Hindi, it is a meaningless conversation.
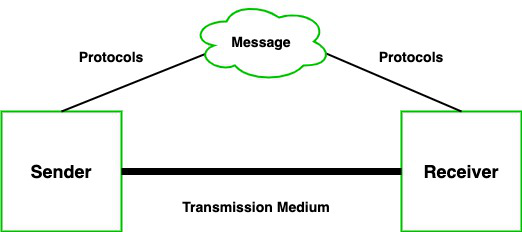
Therefore, there are some set of rules (protocols) that is followed by every computer connected to the internet and they are:
- TCP(Transmission Control Protocol): It is responsible for dividing messages into packets on the source computer and reassembling the received packet at the destination or recipient computer. It also makes sure that the packets have the information about the source of the message data, the destination of the message data, the sequence in which the message data should be re-assembled, and checks if the message has been sent correctly to the specific destination.
- IP(Internet Protocol): Do You ever wonder how does computer determine which packet belongs to which device. What happens if the message you sent to your friend is received by your father? Scary Right. Well! IP is responsible for handling the address of the destination computer so that each packet is sent to its proper destination.
Type of data communication
As we know that data communication is communication in which we can send or receive data from one device to another. The data communication is divided into three types:
- Simplex Communication: It is one-way communication or we can say that unidirectional communication in which one device only receives and another device only sends data and devices uses their entire capacity in transmission. For example, IoT, entering data using a keyboard, listing music using a speaker, etc.
- Half Duplex communication: It is a two-way communication or we can say that it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send and receive data but not at the same time. When one device is sending data then another device is only receiving and vice-versa. For example, walkie-talkie.
- Full-duplex communication: It is a two-way communication or we can say that it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send and receive data at the same time. For example, mobile phones, landlines, etc.
Comments
Post a Comment